Using arrays of floating-point variables
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
| IBM ILOG Solver User's Manual > More on Modeling > Using Constrained Floating-Point Variables: Modeling Equations > Using arrays of floating-point variables |
Using arrays of floating-point variables |
INDEX
 PREVIOUS
NEXT
PREVIOUS
NEXT
|
You may often find it useful to design a model of your problem that organizes the unknowns into arrays of variables. Concert Technology provides a class of arrays for numerical variables, IloNumVarArray.
Let's assume two constrained floating-point variables, x and y, and one constrained integer variable, k. These three variables use the following intervals as their domains:
x 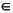 [-5, 108]
[-5, 108]
y 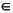 [0, 108]
[0, 108]
k 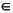 [-1000, 1000]
[-1000, 1000]
Let's also assume the following system of equations must be solved:
x3 + 10x = yx - 2k
kx + 7.7y = 2.4
(k - 1)y+1 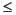 10
10
(log(y + 2x + 12.) 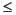 k + 5.
k + 5. 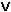 y
y 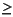 k2)
k2) 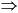 (x
(x 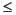 0.
0. 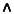 y
y 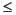 1)
1)
x 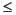 0
0 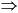 k > 3
k > 3
The solution is:
x = -1.285057857952
y = 0.9792508352872
k = 4
The complete program follows:
#include <ilsolver/ilosolverfloat.h>
ILOSTLBEGIN
int main(){
IloEnv env;
try {
IloModel model(env);
IloNumVar x(env, -5, 1e8);
IloNumVar y(env, 0, 1e8);
IloIntVar k(env, -1000, 1000);
model.add(IloPower(x,3) + 10*x == IloPower(y, x) - IloPower(2, k));
model.add(k*x + 7.7*y == 2.4);
model.add(IloPower(k-1, y+1) <= 10);
model.add(IloIfThen(env, IloLog(y + 2*x + 12) <= k + 5 || y >= k*k, x <= 0 && y <= 1));
model.add(IloIfThen(env, x <= 0, k > 3));
IloNumVarArray vars(env, 2, x, y);
IloSolver solver(env);
solver.out().precision(16);
solver.extract(model);
if (solver.solve(IloGenerateBounds(env, vars, .1))) {
solver.out() << "x = " << solver.getFloatVar(x) << endl;
solver.out() << "y = " << solver.getFloatVar(y) << endl;
solver.out() << "k = " << solver.getIntVar(k) << endl;
}
solver.printInformation();
}
catch (IloException& ex) {
cout << "Error: " << ex << endl;
}
env.end();
return 0;
}
Here's the output of the program.
x = [-1.285057857942743..-1.285057857928474] y = [0.9792508352918879..0.979250835302613] k = [4] |
The complete program is available online in the YourSolverHome/examples/src/narin.cpp file.
| © Copyright IBM Corp. 1987, 2009. Legal terms. | PREVIOUS NEXT |